Without the gallbladder’s role in bile storage and release, the digestion of fats becomes less efficient. This can lead to difficulties in absorbing fat-soluble vitamins like A, D, E, and K, as well as discomfort and digestive issues.
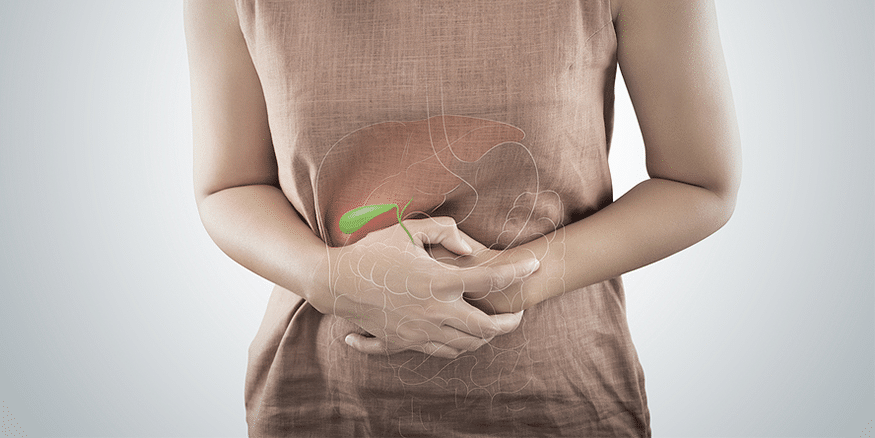
Maintaining the health of the gallbladder is paramount for overall digestive well-being. A malfunctioning gallbladder can lead to various health issues that affect not only digestion but also the surrounding organs and systems. Two of the most common problems associated with the gallbladder are the formation of gallstones and inflammation, known as cholecystitis.
Understanding the signs and symptoms of gallbladder issues is essential for timely intervention and treatment. This knowledge empowers individuals to take charge of their health and make informed decisions to prevent complications.
It’s important to remember that while minor digestive discomfort can be common, persistent or severe symptoms warrant medical attention. By learning about the gallbladder’s role and staying vigilant about its well-being, you can take proactive steps toward maintaining optimal digestive health.
Common Gallbladder Issues
The gallbladder, while integral to the digestive process, can also be susceptible to several common issues that can disrupt its normal function. Being aware of these issues and their associated symptoms is essential for timely diagnosis and treatment.
1. Gallstones
Gallstones are perhaps the most well-known and prevalent gallbladder-related problem. These are solid particles that form in the gallbladder from cholesterol, bilirubin, and other substances found in bile.
Gallstones can vary in size from tiny grains to larger masses, and they can obstruct the normal flow of bile, leading to discomfort and complications.
Recommended: How Do You Sleep With Gallbladder Disease?
Gallstones form when there is an imbalance in the components of bile, leading to the crystallization of cholesterol or bilirubin. These stones can remain in the gallbladder or migrate to the bile ducts.
Common symptoms of gallstones include sudden and intense pain in the upper right abdomen, often radiating to the back or right shoulder blade. Other symptoms may include nausea, vomiting, bloating, and a feeling of fullness after meals.
Certain factors increase the risk of developing gallstones, including obesity, a diet high in fat and cholesterol, rapid weight loss, and genetic predisposition.
2. Cholecystitis
Cholecystitis refers to the inflammation of the gallbladder, often caused by gallstones blocking the cystic duct. This condition can range from acute (sudden and severe) to chronic (recurring over time).
When a gallstone obstructs the cystic duct, it can cause the bile to become trapped in the gallbladder, leading to inflammation and potentially infection.
Cholecystitis can be triggered by gallstones, but it can also be caused by infections, certain medications, and other medical conditions.
Symptoms of cholecystitis include severe abdominal pain, tenderness over the right side of the abdomen, fever, and sometimes jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes).
Understanding these common gallbladder issues is crucial for recognizing when your gallbladder might be affecting your health. The symptoms associated with these problems can range from mild discomfort to severe pain, and they often warrant medical attention.
How Do You Know If Your Gallbladder Is Affecting You?
Recognizing the signs that your gallbladder might be causing issues is vital for prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment. The gallbladder-related symptoms can range from subtle discomfort to more pronounced pain and digestive disturbances.
Early Warning Signs
- Indigestion and Bloating: Persistent indigestion, bloating, and a feeling of fullness after consuming fatty foods might indicate gallbladder issues. If you notice these symptoms occurring frequently, it’s important to pay attention.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Unexplained nausea and occasional vomiting, particularly after meals, could be a sign that your gallbladder is not functioning optimally.
- Belching and Gas: Experiencing excessive belching and gas, especially in conjunction with other digestive symptoms, might be indicative of gallbladder troubles.
Recommended: Does Sleep Help The Gallbladder?
Pain and Discomfort
- Location and Type of Pain: Gallbladder-related pain typically occurs in the upper right abdomen, just below the ribcage. It can be described as a sharp or cramping pain.
- Radiation of Pain: The pain can radiate to the back or right shoulder blade. This radiation happens due to the shared nerve pathways between these areas.
- Duration and Intensity: Gallbladder pain can be intermittent or constant, and it might range from mild discomfort to intense, incapacitating pain.
Changes in Bowel Movements
- Diarrhea: Some gallbladder issues can lead to changes in bowel habits, such as diarrhea. This could be linked to the impaired digestion of fats.
- Light-Colored Stools: Stools that appear pale or clay-colored might suggest a lack of bile reaching the intestines, which is a potential gallbladder-related concern.
Other Symptoms
- Jaundice: If your skin and the whites of your eyes start to turn yellow, this might indicate a blockage in the bile ducts, which can be related to gallbladder issues.
- Fever and Chills: Inflammation of the gallbladder can lead to fever and chills, especially if it progresses to cholecystitis.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Severe gallbladder problems might lead to unintended weight loss due to reduced nutrient absorption and changes in eating patterns.
Recognizing these signs and symptoms is an essential step in gauging whether your gallbladder might be affecting your health. If you experience persistent or severe symptoms, it’s advisable to consult a medical professional.

Diagnosing Gallbladder Issues
When you suspect that your gallbladder might be causing problems due to the symptoms you’re experiencing, seeking a proper diagnosis is crucial. Healthcare professionals employ a combination of methods to accurately diagnose gallbladder issues and determine the best course of action.
1. Medical History and Physical Examination
- Patient History: Your healthcare provider will inquire about your symptoms, their duration, and any factors that might exacerbate or alleviate them. Information about your diet, lifestyle, and medical history is also essential for proper evaluation.
- Physical Examination: A thorough physical examination, including palpation of the abdomen, can help identify tenderness, pain, or other signs of gallbladder-related problems.
Recommended: Can Cholecystitis Cause Insomnia?
2. Imaging Tests
- Ultrasound: Ultrasound imaging is commonly used to visualize the gallbladder and detect gallstones. Sound waves create detailed images that can reveal the presence, size, and location of gallstones.
- CT Scan: A computed tomography (CT) scan provides cross-sectional images of the body and can help identify gallstones, inflammation, or other issues in and around the gallbladder.
- HIDA Scan: A hepatobiliary iminodiacetic acid (HIDA) scan involves injecting a radioactive tracer into your bloodstream. This tracer is taken up by the liver and excreted into the bile. The scan tracks the tracer’s movement through the liver, bile ducts, and gallbladder, helping evaluate gallbladder function.
3. Blood Tests
- Liver Function Tests: Blood tests can measure levels of enzymes and other substances that indicate the health of the liver and gallbladder. Elevated levels might suggest inflammation or obstruction.
- Bilirubin Levels: Elevated bilirubin levels can indicate a blockage in the bile ducts, potentially caused by gallstones.
Accurate diagnosis is crucial as it guides the appropriate treatment plan. Depending on the diagnosis, your healthcare provider will recommend the most suitable interventions to alleviate your symptoms and address the underlying issue.
Recommended: Gallbladder And Sleep Problems: All You Need To Know
Seeking Medical Help
When it comes to your gallbladder health, knowing when to consult a healthcare professional is essential for receiving appropriate care and preventing potential complications. While mild digestive discomfort can sometimes be attributed to various factors, certain symptoms warrant prompt medical attention.
When to Consult a Doctor
- Persistent Symptoms: If you experience persistent symptoms such as abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, or changes in bowel habits that last for several days or weeks, it’s important to consult a doctor. Ignoring these symptoms might lead to worsened conditions.
- Severe Pain: If you encounter sudden and severe pain in the upper right abdomen, especially if it radiates to the back or shoulder, seek medical help immediately. Severe pain could indicate a more serious issue like a gallstone lodged in a bile duct.
Importance of Early Diagnosis
- Preventing Complications: Gallbladder issues left untreated can lead to complications such as infection, inflammation, and even a blocked bile duct. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent these complications from worsening.
- Treatment Options: Diagnosing the root cause of your symptoms is crucial for determining the appropriate treatment plan. Gallbladder problems can vary, and the recommended approach might range from lifestyle changes to surgical intervention.
Visiting a healthcare professional early not only addresses your current symptoms but also provides you with the necessary guidance for managing your health moving forward. Your doctor will be able to recommend tests, interpret results, and develop a personalized treatment strategy based on your specific situation.
Treatment Options
When it comes to addressing gallbladder issues, there are several treatment approaches available, ranging from lifestyle changes to medical interventions. The choice of treatment depends on the specific diagnosis, the severity of your symptoms, and your overall health.
Recommended: Can Steroid Injections Cause Insomnia?
Lifestyle Changes
- Dietary Adjustments: Making changes to your diet can be particularly beneficial for managing gallbladder problems. Reducing your intake of fatty, fried, and processed foods can ease the workload on your gallbladder. Incorporating more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins into your diet can support digestive health.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight is important for gallbladder health. Gradual and sustainable weight loss, if needed, can help reduce the risk of gallstone formation.
Medications
- Pain Relief: Over-the-counter pain medications can provide relief from mild to moderate gallbladder-related pain. However, these medications should only be used under a healthcare professional’s guidance.
- Dissolving Gallstones: In some cases, certain medications can be prescribed to help dissolve gallstones. These medications work best for small cholesterol-based stones and might require several months of treatment.
Surgical Interventions
- Cholecystectomy: A cholecystectomy is the surgical removal of the gallbladder. This procedure is often recommended for individuals with recurrent gallstones, severe gallbladder inflammation (cholecystitis), or other gallbladder-related complications. Cholecystectomy can be performed using traditional open surgery or minimally invasive laparoscopic techniques.
- Minimally Invasive Techniques: Laparoscopic surgery involves making small incisions and using specialized tools and a camera to remove the gallbladder. This approach generally results in a quicker recovery and less scarring compared to open surgery.
The choice of treatment will depend on factors such as the underlying issue, your overall health, and the severity of your symptoms. Your healthcare provider will guide you through the options, discussing the potential benefits, risks, and expected outcomes.
In cases of severe inflammation, infection, or blockages, prompt medical attention and intervention might be required to prevent further complications. It’s important to follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations closely to ensure the best possible outcome for your gallbladder health.
Preventing Gallbladder Issues
Taking proactive steps to maintain your gallbladder health is essential for preventing future issues and promoting overall well-being. By adopting certain lifestyle habits and making informed choices, you can significantly reduce the risk of gallbladder-related problems.
Recommended: Can too much levothyroxine cause insomnia?
Healthy Eating Habits
- Balanced Diet: Embrace a balanced and nutritious diet that includes a variety of foods from different food groups. Focus on whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats while limiting your consumption of saturated and trans fats.
- Adequate Fiber Intake: A high-fiber diet can aid digestion and help prevent the formation of gallstones. Whole grains, legumes, fruits, and vegetables are excellent sources of dietary fiber.
Regular Exercise
- Benefits for Gallbladder Health: Regular physical activity can contribute to maintaining a healthy weight and reducing the risk of gallstone formation. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
Managing Risk Factors
- Obesity and Weight Loss: Obesity is a significant risk factor for gallstone formation. If you’re overweight, focus on gradual and sustainable weight loss through a combination of healthy eating and increased physical activity.
- Gradual Weight Management: Rapid weight loss or crash diets can increase the risk of gallstones. Aim for slow, steady weight loss to minimize the strain on your gallbladder.
- Avoid Extreme Diets: Extreme diets that severely restrict fat intake might disrupt the gallbladder’s function. Instead, opt for a balanced approach to fat consumption.
By incorporating these preventive measures into your lifestyle, you can reduce the likelihood of developing gallbladder-related problems and promote your overall digestive health.
Recommended: Can Castor Oil Boost Ovulation?
Remember that maintaining a healthy weight, adopting a balanced diet, and staying physically active have far-reaching benefits beyond just the gallbladder – they contribute to your overall well-being and quality of life.
Conclusion
In understanding the significance of the gallbladder’s role and the potential impact of its issues, we empower ourselves to prioritize digestive health. Recognizing symptoms, seeking timely medical attention, and embracing preventive measures are key to a gallbladder-friendly lifestyle. By making informed choices, we can safeguard our well-being, ensuring optimal digestion and overall vitality.
[…] Recommended: How Do You Know If Your Gallbladder Is Affecting You? […]
[…] Recommended: How Do You Know If Your Gallbladder Is Affecting You? […]