Ever wondered about the tiny things that help make babies? Well, two important players in this story are semen and sperm. They’re like the superheroes of the male reproductive system, each with its own job to help create new life.
Semen and sperm often get mixed up in conversations, but they’re actually different things. Semen is like a protective fluid that carries sperm, which are tiny cells, on an amazing adventure.
Knowing the difference between semen and sperm is like knowing the difference between a vehicle and its fuel. Understanding what each does helps us grasp how babies are made. Plus, it’s really helpful for anyone thinking about starting a family or learning about the human body.
Recommended: Can Castor Oil Boost Ovulation?
In this guide, we’re going to explore what semen and sperm are made of and discover how these two work together to kickstart the baby-making process. Let’s dive in!
What is Sperm?
Sperm might be tiny, but these microscopic cells are essential in the baby-making process. They’re the male reproductive cells, shaped like tiny tadpoles, and they pack a powerful punch when it comes to fertilization.

Role in Reproduction
The primary mission of sperm is to fertilize a female egg, kickstarting the creation of a new life. When released inside a woman’s body, they embarks on an incredible journey, racing to reach the egg for a chance to fuse with it.
Recommended: Can Straining To Poop Cause Cervix To Open?
Formation of Sperm (Spermatogenesis)
Sperm cells aren’t made overnight. They undergo a fascinating process called spermatogenesis. It happens in the testicles and takes around 64 to 72 days to complete. Special cells called germ cells transform into sperm through multiple stages of development.
Characteristics and Functions
Sperm cells are designed for one job: to swim! Their unique tail propels them forward, navigating through the female reproductive tract to find the egg. While they’re on this journey, they carry the genetic material from the male – half of the information needed to create a new human.
Recommended: Can You Get STD From Toilet Water Splashing?
Lifespan and Survival
Once released, sperm have a limited lifespan. They can survive for a few days in the female reproductive system, waiting for the right moment to encounter an egg. However, only one lucky sperm gets the chance to fuse with the egg and kick off the miraculous process of conception.
Quantity and Release
When a man ejaculates, he releases millions of sperm in semen. But despite the large numbers, only a few hundred make it close to the egg. It’s like a marathon where only a handful reach the finish line!
Recommended: 6 Reasons Why My Vagina Smell Like A Fish
Understanding sperm and its incredible capabilities gives us a peek into the intricate workings of reproduction. These tiny cells may be small in size, but they play a huge role in the miracle of life.
What is Semen?
Semen is not just a simple fluid; it’s a complex mixture with a critical role in reproduction. This fluid, often mistaken for sperm, is actually a combination of various substances produced by different glands in the male reproductive system. It includes fluids from the seminal vesicles, prostate gland, and other accessory glands.

Components of Semen
Beyond sperm cells, semen contains a variety of elements essential for their survival and function. These components include enzymes, fructose (a sugar providing energy for sperm), and various proteins. Each component serves a specific purpose, from nourishing and protecting sperm to aiding their movement.
Purpose and Functions
Semen serves as a protective and nourishing vehicle for sperm. It provides a medium for sperm cells to travel through the female reproductive tract, offering them a safe environment and energy to reach the egg.
Additionally, the components in semen help neutralize the acidic environment of the female reproductive system, creating a more favorable environment for sperm survival.
Production and Release
The production of semen involves a coordinated effort among different glands. The seminal vesicles, prostate gland, and other contributing glands produce their respective fluids, which combine to form semen. During ejaculation, the muscles in the male reproductive system contract to propel semen through the urethra and out of the body.
Role in Fertilization
While sperm cells are the key players in fertilization, semen plays a crucial supporting role. It acts as a transport medium, carrying and protecting sperm on their journey to meet the egg. Without the supportive environment provided by semen, sperm would struggle to survive the harsh conditions of the female reproductive tract.
Quantity and Quality
The quantity and quality of semen can vary among individuals and can be influenced by various factors such as age, health, and lifestyle. Understanding semen quality is vital for assessing fertility and reproductive health.
Recommended: Vaginal Itching: 20 Possible Causes
Comprehending the complexity and significance of semen beyond its role as a carrier for sperm enriches our understanding of the male reproductive process. It’s not just a fluid; it’s a finely tuned mixture crucial for the success of sperm and, ultimately, the creation of new life.
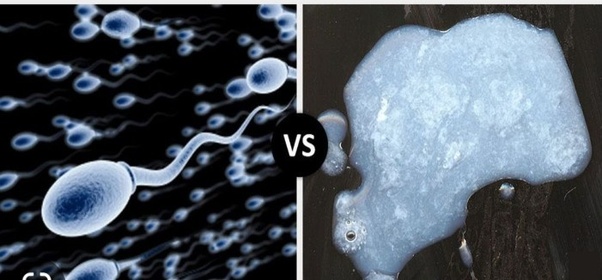
Differences Between Sperm and Semen
Sperm and semen are related to male reproductive biology, but they are not the same thing!
Sperm
- Sperm are the male reproductive cells.
- They are produced in the testes through a process called spermatogenesis.
- Sperm are tiny, motile cells with a single nucleus, designed for fertilizing a female egg.
- They contain genetic material (DNA) and are responsible for carrying the father’s genetic information to fertilize the egg during sexual reproduction.
- Sperm cells make up a small portion of semen.
Semen
- Semen is the fluid that carries and nourishes the sperm cells.
- It’s a viscous, whitish fluid ejaculated from the male reproductive tract during ejaculation.
- Semen is composed of fluids from various glands, including the seminal vesicles, prostate gland, and Cowper’s gland.
- It provides a medium for sperm cells to travel and survive outside the male body.
- Semen contains nutrients and substances that support and protect the sperm on their journey to the female reproductive system.
Recommended: Can Pregnant Women Drink Thai Tea?
In summary, sperm are the actual male reproductive cells, while semen is the fluid that carries and supports these cells during ejaculation. Semen provides a protective and nourishing environment for sperm, allowing them to travel through the female reproductive system to potentially fertilize an egg.

Importance of Understanding the Differences
1. Reproductive Health Awareness
- Optimal Timing for Conception: Knowing the roles of semen and sperm helps individuals understand the best times for conception, optimizing chances of successful pregnancy.
- Fertility Awareness: Understanding the factors influencing sperm and semen health aids in recognizing potential fertility issues, and encouraging timely intervention if needed.
2. Informed Decision Making
Family Planning: Knowledge about semen and sperm assists couples in making informed decisions regarding family planning, fertility treatments, or contraception methods.
3. Healthcare and Lifestyle Choices
- Promoting Healthy Habits: Awareness of how lifestyle choices affect sperm and semen health motivates individuals to adopt healthier habits, improving overall reproductive health.
- Seeking Medical Help: Recognizing signs of potential reproductive issues encourages seeking medical advice early, potentially addressing concerns before they become serious.
4. Fostering Reproductive Equality
Empowering Discussions: Understanding these differences promotes open and informed discussions about reproductive health, fostering equality and shared responsibility in family planning.
5. Supporting Fertility Treatment
Assistance in Treatment: People undergoing fertility treatments benefit from understanding the role of semen and sperm, aiding in their active participation in treatment plans.
6. Advancing Research and Development
Research and Innovation: Understanding the complexities of semen and sperm encourages research into reproductive health, leading to advancements in treatments and technologies.
7. Empowering Individuals
Knowledge for Empowerment: Equipping individuals with accurate information empowers them to take charge of their reproductive health, reducing anxiety and misconceptions.
Recommended: 7 Ways on How To Tighten The Vagina.
Understanding the differences between semen and sperm extends beyond basic knowledge; it’s a cornerstone for informed choices, proactive health management, and fostering supportive reproductive environments.
By embracing this understanding, People can navigate their reproductive journey with confidence, seeking assistance when needed and making decisions that align with their aspirations for a healthy family life.
The Journey of Sperm and Semen
Let’s look at how sperm and semen work together to perform their function…
1. Release and Transportation
When a man ejaculates, semen – a mix of fluids from various glands along with sperm cells – is released from the penis. This ejaculation is propelled by muscular contractions in the male reproductive system. The semen travels through the urethra and exits the body. During this process, millions of sperm begin their incredible quest toward fertilization.
2. Navigating the Female Reproductive Tract
Once inside the female body, semen and sperm face a challenging journey. The female reproductive tract is designed to filter and support the strongest sperm on their mission to find the egg.
Semen provides a protective environment for sperm, shielding them from the acidic conditions of the vagina. The fructose in semen provides energy to fuel the sperm’s journey.
Sperm swim through the cervix and into the uterus, propelled by their tail movements. Then, they navigate through the fallopian tubes, where the egg is usually waiting for fertilization.
Fertilization Process
If there’s an egg present in the fallopian tube, the race intensifies. Only one lucky and determined sperm out of millions manages to penetrate the egg’s outer layer. Once a sperm successfully fuses with the egg, fertilization occurs, marking the beginning of a new life.
Survival and Lifespan
While millions of sperm embark on this journey, only a few hundred make it near the egg. The rest perish along the way. Sperm can survive for a few days within the female reproductive tract, waiting for the egg to be released.
Recommended: Can You Drink Loaded Teas While Pregnant?
The journey of sperm and semen is fraught with challenges. From navigating the complex female reproductive system to contending with other sperm, only the strongest and fastest sperm complete the journey to fertilize the egg.

Factors Affecting Sperm and Semen
1. Environmental Influences
- Temperature: Sperm production thrives in a slightly lower temperature than the body’s norm. Increased testicular heat due to tight clothing, saunas, or prolonged sitting can hamper sperm production.
- Chemical Exposure: Contact with certain chemicals or toxins in the environment, such as pesticides or industrial chemicals, may negatively impact sperm quality and function.
2. Health and Lifestyle Factors
- Nutrition: A balanced diet rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals positively influences semen quality. Conversely, poor nutrition, excessive alcohol consumption, or smoking can harm sperm production and quality.
- Exercise and Weight: Maintaining a healthy weight and moderate exercise contribute to better reproductive health. Obesity or excessive exercise can affect hormone levels and sperm production.
- Stress: High-stress levels can affect hormonal balance, potentially impacting sperm production and quality.
3. Medical Conditions Impacting Sperm and Semen
- Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs): Certain STIs can affect sperm health and fertility if left untreated. Seeking timely medical care is crucial.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Conditions like hypogonadism or hormonal imbalances can hinder sperm production and quality.
- Genetic Factors: Genetic abnormalities or conditions such as Klinefelter syndrome can affect sperm production and function.
4. Age and Reproductive Health
- Age: Sperm quality tends to decline with age. While men can produce sperm throughout their lives, advanced age can lead to decreased sperm motility and DNA damage.
- Reproductive Health Practices: Prolonged abstinence or frequent ejaculation might influence sperm count. Balancing these factors can impact semen quality.
Recommended: Air Pollution And It’s Health Consequences.
Understanding these factors highlights the delicate balance required for optimal sperm and semen health. Lifestyle choices, environmental exposures, and medical conditions all play significant roles in shaping reproductive health. Monitoring and addressing these factors can positively impact fertility and overall reproductive well-being.
Seeking medical advice for concerns regarding sperm and semen health is crucial for individuals planning for conception or facing fertility issues.
Common Misconceptions
1. Misconception: More Semen Means More Fertile
Fact: While the volume of semen ejaculated may vary among individuals, it doesn’t necessarily correlate with fertility. Fertility depends on sperm count, motility, and quality rather than the amount of semen.
2. Misconception: All Semen is the Same
Fact: Semen can differ in composition and quality. Factors like diet, overall health, and lifestyle choices can affect the composition of semen, potentially influencing sperm health.
3. Misconception: Every Sperm is Perfectly Healthy
Fact: Not all sperm are created equal. Even in healthy males, a significant portion of sperm may have abnormalities. A high number of abnormal sperm can affect fertility.
4. Misconception: Tight Clothing Causes Infertility
Fact: While prolonged exposure to excessive heat can temporarily affect sperm production, wearing tight clothing is unlikely to cause long-term infertility. However, it’s advisable to avoid excessive heat around the testicles for extended periods.
FAQs
What is the difference between semen and sperm?
Semen is a fluid that contains sperm along with other components, while sperm are the microscopic cells responsible for fertilization within the semen.
Do semen and sperm mean the same thing?
No, semen is the fluid that carries sperm. Sperm are the individual cells within semen, responsible for fertilizing an egg.
Can semen exist without sperm?
No, semen primarily consists of sperm cells. While other fluids contribute to semen, sperm cells are a crucial component for reproduction.
How do semen and sperm function during conception?
Semen provides a protective environment for sperm, aiding their travel to reach an egg. Sperm, upon reaching the egg, attempts fertilization.
Does the quantity of semen indicate fertility?
Fertility depends more on sperm count, motility, and quality rather than the volume of semen ejaculated.
Can lifestyle choices affect sperm and semen health?
Yes, lifestyle factors such as diet, exercise, smoking, and exposure to toxins can significantly impact the quality and health of both sperm and semen.
Can problems with semen or sperm cause infertility?
Yes, issues with either semen quality or sperm health can lead to difficulties in conception and contribute to infertility in some cases.
What medical conditions can affect sperm and semen?
Medical conditions such as infections, hormonal imbalances, genetic disorders, or anatomical issues can impact both sperm production and semen quality.
Is age a factor in sperm and semen health?
Yes, advancing age can affect sperm quality, potentially impacting fertility and increasing the risk of certain genetic conditions in offspring.
How can one improve sperm and semen health?
Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding harmful substances, can positively influence sperm and semen health.
Conclusion
Comprehending the differences between semen and sperm is crucial for informed reproductive decisions. Acknowledging their distinct roles empowers individuals in family planning, encourages proactive health choices, and fosters open discussions.
By understanding these tiny yet vital components, we pave the way for better reproductive health and informed choices, ultimately contributing to the profound journey of creating and nurturing new life.
[…] Recommended: Differences Between Semen And Sperm […]
[…] Recommended: Differences Between Semen And Sperm […]
[…] Recommended: Differences Between Semen And Sperm […]
[…] Recommended: Differences Between Semen And Sperm […]