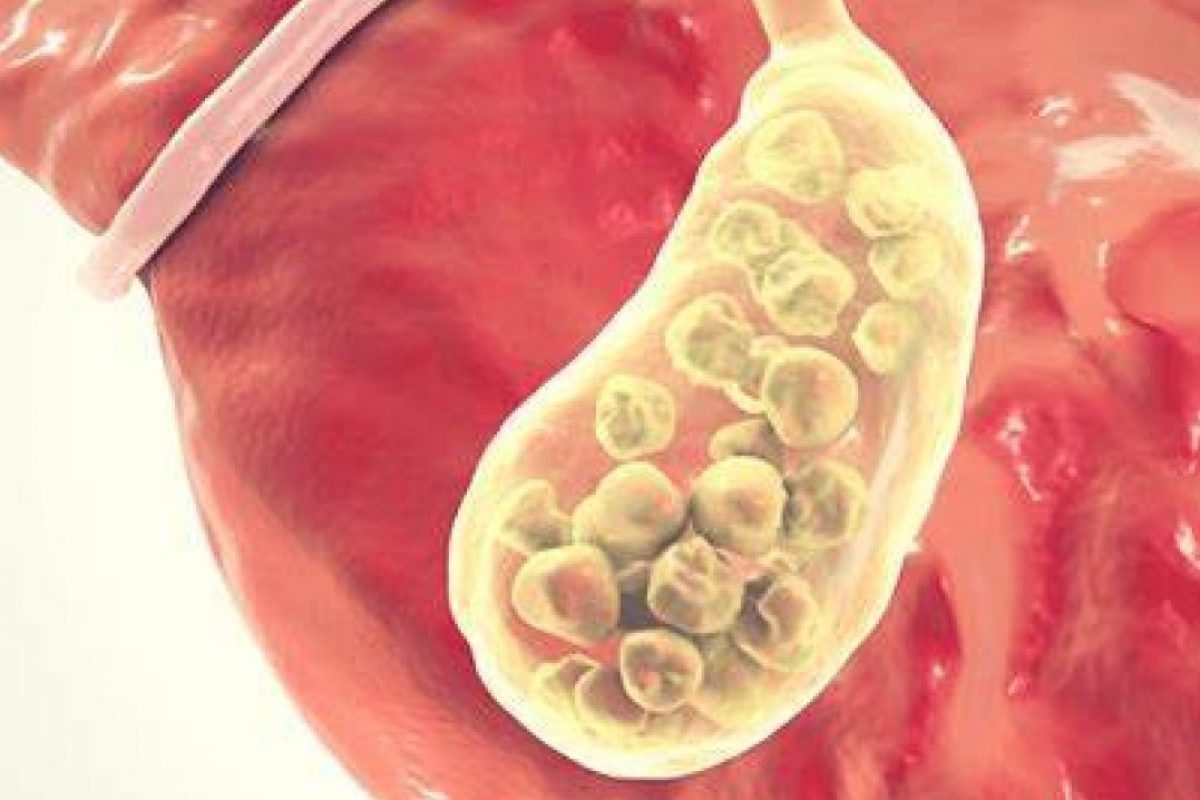
The gallbladder is a small pear-shaped organ tucked right below the liver in the upper right abdomen. Though it might not be as widely discussed as the heart or lungs, its function is paramount to our digestive system.
It’s responsible for storing bile, a digestive fluid produced by the liver. Whenever we eat foods, especially those rich in fat, the gallbladder releases this bile into the small intestine, helping in the emulsification and digestion of fats.
Inflammation of the gallbladder, known medically as “cholecystitis,” can be an unsettling condition. This inflammation is most commonly caused by gallstones blocking the bile ducts, which prevents bile from flowing out of the gallbladder. This blockage causes the gallbladder to swell, leading to sharp pain, potential infection, and a range of other symptoms.
If not addressed in time, an inflamed gallbladder can lead to severe complications, some of which may be life-threatening. Recognizing the signs of this condition and understanding its ramifications is essential for anyone aiming to maintain optimal digestive health.
How Long Can a Gallbladder Stay Inflamed?
The duration of gallbladder inflammation, or cholecystitis, can vary depending on its type and other underlying factors:
1. Acute Cholecystitis: Sudden and Intense
Acute cholecystitis refers to the sudden inflammation of the gallbladder, typically resulting from a gallstone blocking the cystic duct. This obstruction prevents bile from exiting the gallbladder, causing it to swell and become inflamed rapidly.
Recommended: How Do Doctors Tell If Your Gallbladder Is Inflamed?
The duration of acute cholecystitis can vary depending on its cause and the timely initiation of treatment. Typically, symptoms of acute cholecystitis can last for several hours to a few days. Without appropriate treatment, the inflammation can become severe, leading to potential complications. Therefore, seeking medical attention promptly is crucial.
2. Chronic Cholecystitis: A Long-standing Battle
Chronic cholecystitis is a prolonged inflammatory condition. Often, it results from repeated episodes of acute cholecystitis. Over time, the gallbladder wall can become thickened, and its function can deteriorate, making it less efficient at storing and releasing bile.
Unlike its acute counterpart, chronic cholecystitis may persist for months or even years. Symptoms might be less intense than those of acute cholecystitis, but they can be more persistent and recurrent. Episodes of pain and discomfort might be interspersed with symptom-free periods.
Over time, if left untreated, the gallbladder can lose its function entirely, leading to a condition called “gallbladder dyskinesia” or “biliary dyskinesia”.
Recommended: What Antibiotics Treat Gallbladder Infections?
Factors Affecting the Duration of Inflammation
1. Severity of the Initial Condition or Cause
- Gallstones Size and Number: Larger or multiple gallstones are more likely to cause significant blockages in the bile ducts, leading to more pronounced inflammation and potentially a longer recovery time.
- Infections: The presence of bacterial infections can exacerbate inflammation, leading to a prolonged inflammatory response.
2. Timeliness and Effectiveness of Treatment
- Early Intervention: Seeking medical attention promptly after the onset of symptoms can lead to quicker diagnosis and treatment, reducing the duration of inflammation.
- Treatment Approach: The chosen treatment method, whether it be dietary changes, medications, or surgical interventions, can influence how quickly inflammation subsides. For instance, in some cases, removing the gallbladder might be the most effective way to resolve chronic inflammation.
3. Overall Health of the Patient
- Immune System Efficiency: A healthy immune system can aid in the body’s ability to combat inflammation and heal more efficiently.
- Co-existing Medical Conditions: Patients with other health issues, especially those related to the liver or digestive system, may experience prolonged inflammation. Conditions like liver cirrhosis or chronic pancreatitis might complicate gallbladder inflammation.
- Age: Older individuals might experience a longer duration of inflammation due to age-related decline in tissue repair and immune response.
Recommended: Can Gallbladder Symptoms Go Away?
4. Presence of Other Underlying Conditions
- Biliary Dyskinesia: This condition, where the gallbladder doesn’t empty correctly, can exacerbate and prolong inflammation.
- Gallbladder Polyps: These benign growths might not cause inflammation directly, but their presence can alter gallbladder function and contribute to prolonged inflammation in conjunction with other factors.
- Bile Duct Abnormalities: Structural issues in the bile ducts can lead to improper bile flow, further prolonging the duration of inflammation.

Potential Complications of Prolonged Inflammation
1. Gallbladder Rupture
- What it is: A perforation or tear in the gallbladder wall.
- Why it happens: Prolonged inflammation can weaken the gallbladder’s walls, making it susceptible to rupture, especially if the cause of inflammation (e.g., gallstones) is not addressed.
- Consequences: If the gallbladder ruptures, bile and potentially infected material can spill into the abdominal cavity, leading to a severe condition called peritonitis which requires immediate medical attention.
2. Infection
- What it is: Bacterial infection in the gallbladder, also known as empyema of the gallbladder.
- Why it happens: When the gallbladder’s outflow is obstructed, bacteria can proliferate in the stagnant bile, leading to an infected gallbladder.
- Consequences: If not treated, the infection can spread to other areas or into the bloodstream, causing sepsis, a life-threatening condition.
Recommended: What Foods Heal The Gallbladder?
3. Spread of Inflammation to Other Parts of the Body
- What it is: Inflammation that begins in the gallbladder but then affects surrounding tissues or organs.
- Affected Areas: Nearby organs such as the liver, pancreas, and bile ducts can become inflamed, leading to conditions like cholangitis (inflammation of the bile ducts) or pancreatitis.
- Consequences: These conditions can have their complications and can further complicate the overall clinical picture, making treatment more challenging.
4. Formation of Gallbladder Abscess
- What it is: A pocket of pus that forms within the gallbladder.
- Why it happens: Persistent inflammation and infection can lead to abscess formation.
- Consequences: An abscess can lead to severe pain and systemic infection. If not addressed, the abscess can rupture, similar to a gallbladder rupture, spreading infected material within the abdominal cavity.
Recommended: Can Gallbladder Pain Wake You Up At Night?
Conclusion
The gallbladder, though a small organ, plays a pivotal role in our digestive system. When inflamed, it not only disrupts its primary function but also poses potential risks to our overall health. Recognizing the signs of gallbladder inflammation and understanding its implications are paramount.
Swift medical intervention can prevent severe complications, preserving not only the health of the gallbladder but the body as a whole. As with many health conditions, awareness, prevention, and timely action are our best allies in maintaining optimal health.
[…] Recommended: How Long Can a Gallbladder Stay Inflamed? […]
[…] Recommended: How Long Can a Gallbladder Stay Inflamed? […]
[…] Recommended: How Long Can a Gallbladder Stay Inflamed? […]