Oral health is a fundamental aspect of overall well-being, often underestimated in its impact on our daily lives. Among the various oral health concerns, gum disease stands out as a prevalent issue affecting millions worldwide. It encompasses two primary conditions: gingivitis and periodontitis, both of which can have far-reaching consequences if left unattended.
While the contagious nature of certain diseases like the flu or the common cold is widely known, the question of whether gum disease can be transmitted from one person to another often sparks curiosity and concern. This aspect of contagion in oral health is pivotal, particularly in understanding how gum disease may spread among individuals.
In exploring the contagious nature of gum disease, we delve into the intricate world of oral bacteria and their ability to be transferred from one person to another. Understanding how these bacteria can travel between individuals sheds light on the importance of proactive measures to curb their transmission.
Recommended: Disadvantages Of Dental Crowns: Risks and Complications
This guide aims to enlighten you on the contagious potential of gum disease. By examining its causes, progression, and factors influencing contagion, we seek to empower you with the knowledge to protect yourself and your loved ones from the risks associated with this prevalent oral health concern.
What Is Gum Disease?
Oral health serves as a window into our overall well-being, and gum disease stands as a significant concern within this realm. It comprises two primary conditions, each with distinct characteristics and implications for oral health: gingivitis and periodontitis.
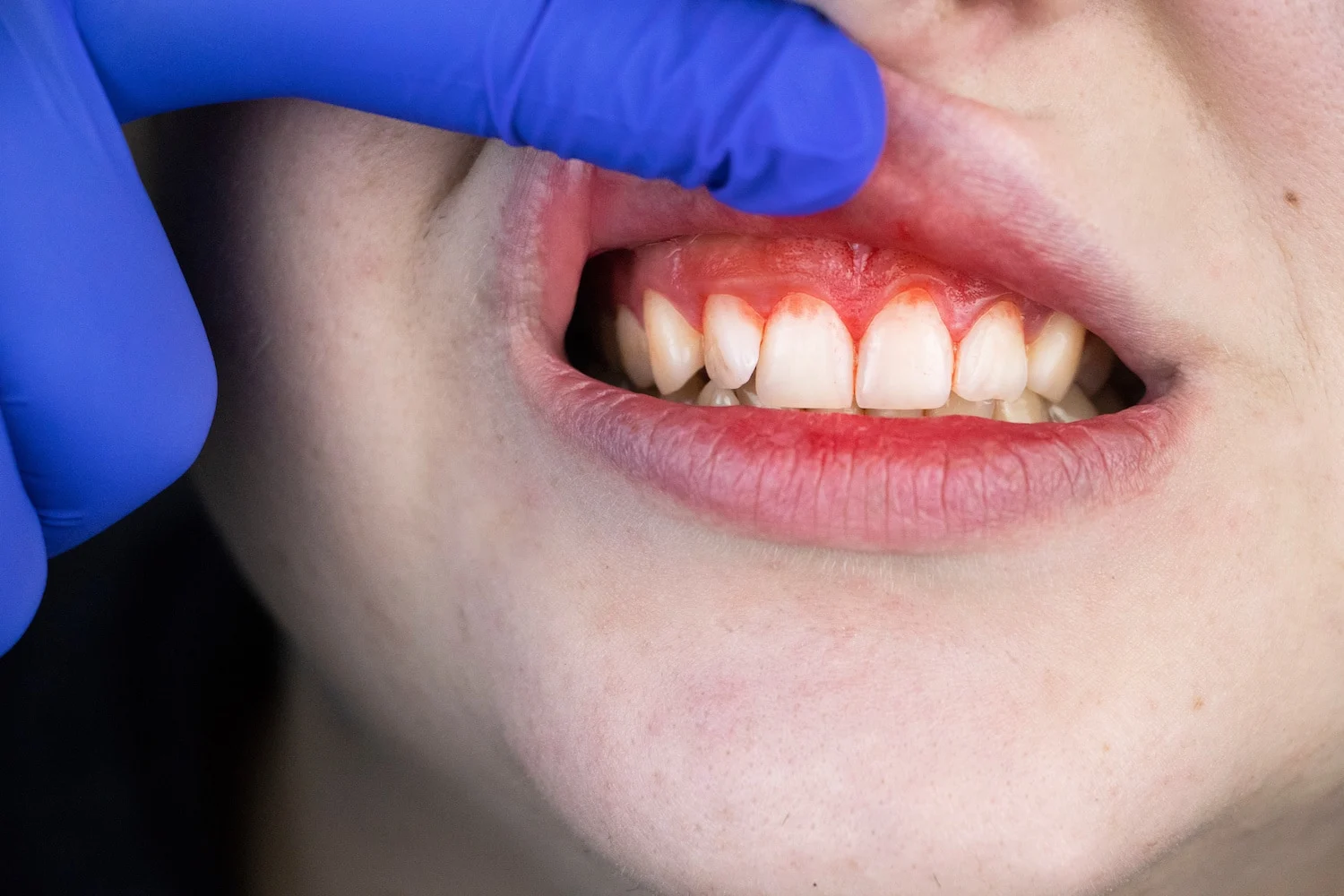
Gingivitis marks the initial stage of gum disease. It arises from the accumulation of plaque, a sticky film consisting of bacteria, on teeth and gums. This buildup irritates the gums, leading to inflammation, redness, swelling, and tenderness. One of the telltale signs of gingivitis is bleeding gums, especially noticeable while brushing or flossing.
Recommended: How To Cure Gum Disease Without a Dentist
If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to a more severe condition known as periodontitis. In this stage, the infection spreads from the gums to the supporting structures of the teeth, including the bone and ligaments. Periodontitis causes gums to pull away from the teeth, forming pockets that accumulate more bacteria and debris. Over time, these pockets deepen, leading to further damage to the bone and ultimately tooth loss.

Gum disease doesn’t confine its effects solely to the mouth. Research has linked periodontal disease to various systemic health issues, including cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, respiratory infections, and complications during pregnancy. The inflammation and bacteria associated with gum disease can potentially impact overall health, making its management crucial beyond oral hygiene.
The cornerstone of preventing and managing gum disease lies in maintaining proper oral hygiene. Regular brushing with fluoride toothpaste, flossing, and using antimicrobial mouth rinses help remove plaque and bacteria, significantly reducing the risk of gum disease development and progression.
In addition to at-home oral care practices, routine dental check-ups play a vital role in preventing gum disease. Dental professionals not only clean teeth thoroughly but also assess gum health, detect early signs of gingivitis or periodontitis, and provide guidance on maintaining optimal oral hygiene.
Recommended: Can You Swallow Spit From ZYN Pouches?
Understanding the stages and implications of gum disease is crucial for you to recognize its signs and take proactive measures to safeguard your oral health.
Is Gum Disease Contagious?
Yes, gum disease can be considered contagious to some extent. The bacteria that cause gum disease can be transmitted through various means, including close contact, sharing utensils, kissing, or even through airborne particles. While not as immediately contagious as a cold or the flu, there’s a potential for the transfer of oral bacteria from one person to another, particularly among close contacts or family members.
However, not everyone exposed to these bacteria will automatically develop gum disease; other factors like individual oral hygiene practices, immune system strength, and genetic predispositions also play significant roles in determining susceptibility to the condition.
The contagious nature of gum disease adds another layer of complexity to its impact on oral health. While we often associate contagion with respiratory illnesses or infections, understanding how gum disease can be transmitted between individuals is crucial in preventing its spread.
Gum disease, particularly periodontitis, involves an abundance of bacteria within the oral cavity. These bacteria, including Porphyromonas gingivalis and Treponema denticola among others, play a pivotal role in the progression and severity of the condition. What makes gum disease potentially contagious is the transfer of these bacteria from one person to another.
Recommended: How Painful Is Tooth Extraction Without Anesthesia?
Various modes of transmission exist for the transfer of oral bacteria associated with gum disease. Close contact, such as kissing, sharing eating utensils, or using the same oral hygiene tools, provides avenues for bacterial exchange. Additionally, airborne particles from activities like coughing or sneezing may also carry oral bacteria.

Research suggests a correlation between individuals living in close proximity, such as family members or intimate partners, and an increased likelihood of sharing oral bacteria. Factors like saliva exchange during kissing, using the same toothbrush holder, or even sharing food can facilitate the transmission of bacteria associated with gum disease.
Recommended: Does Chamomile Tea Stain Teeth?
While the transfer of oral bacteria between individuals occurs more readily in close contacts, it’s important to note that not everyone exposed to these bacteria will automatically develop gum disease. Factors like an individual’s immune system, overall oral health practices, and genetic predispositions play significant roles in determining susceptibility to the development or progression of gum disease.
Despite the potential for bacterial transmission, preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of spreading gum disease. Practicing good oral hygiene, including regular brushing, flossing, and using antimicrobial mouth rinses, helps minimize bacterial buildup. Avoiding sharing oral hygiene tools and maintaining overall health can also contribute to reducing the chances of bacterial exchange.
Factors Affecting The Transmission Of Gum Disease
Understanding the transmission dynamics of gum disease involves considering multiple factors that influence the likelihood of bacterial exchange and the subsequent development or progression of the condition.
1. Oral Hygiene Practices
Individual oral hygiene habits play a crucial role in both the development and potential transmission of gum disease. Those with poor oral hygiene, characterized by irregular brushing and flossing, are more likely to harbor larger amounts of bacteria in their mouths, thereby increasing the risk of transmitting these bacteria to others.
2. Compromised Immune Systems
People with compromised immune systems face heightened risks concerning the spread and severity of gum disease. A weakened immune response can make it harder for the body to fight off infections, including oral bacterial infections associated with gum disease. This increases susceptibility to developing gum disease and elevates the risk of transmitting bacteria to others.
2. Genetic Predispositions
Genetic factors can influence a person’s susceptibility to gum disease. Certain genetic variations may affect your body’s immune response, making you more prone to developing severe forms of gum disease. Consequently, people with a genetic predisposition may be more likely to transmit oral bacteria associated with gum disease to their close contacts.
Recommended: Can I Drink Iced Tea After Tooth Extraction?
3. Overall Health Status
The overall health and systemic conditions of an individual can also impact the transmission of gum disease. Conditions such as diabetes or cardiovascular diseases, which are linked to gum disease, can exacerbate oral health issues and increase the likelihood of transmitting oral bacteria to others.
4. Age and Environmental Factors
Age can be a contributing factor in both the susceptibility to gum disease and the potential for contagion. Children, for instance, might be more susceptible due to developing immune systems and still developing oral hygiene habits.
Moreover, environmental factors like living conditions and exposure to tobacco smoke can influence the spread of gum disease among individuals.

Prevention and Control Of Gum Disease Transmission
Preventing the transmission of gum disease involves adopting proactive measures that protect people from developing the condition and minimize the risk of spreading oral bacteria to others.
1. Good Oral Hygiene
Maintaining excellent oral hygiene practices stands as the cornerstone of preventing gum disease transmission. Regular brushing at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste helps remove plaque and bacteria, while daily flossing reaches areas between teeth where plaque can accumulate. Also, using antimicrobial mouth rinses can further reduce bacterial growth and aid in preventing gum disease.
2. Personal Oral Care Tools
Encouraging others to use their personal oral care tools is crucial in preventing the exchange of bacteria. Each person should have their own toothbrush, avoiding sharing these tools to prevent the potential transfer of oral bacteria.
Recommended: Can Wisdom Teeth Cause TMJ?
3. Regular Dental Check-ups
Scheduled visits to the dentist are pivotal in preventing gum disease. Professional dental cleanings help remove plaque and tartar buildup that regular brushing and flossing may miss. Moreover, dental professionals can identify early signs of gum disease and provide guidance on optimal oral hygiene practices.
4. Healthy Lifestyle Habits
Adopting a healthy lifestyle contributes significantly to oral health and reduces the risk of gum disease transmission. Avoiding tobacco products and maintaining a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins supports overall oral health and boosts the body’s immune system.
5. Awareness and Education
Promoting awareness and education about gum disease and its contagious nature is key. Educating people about the importance of good oral hygiene, the risks associated with gum disease transmission, and the preventive measures they can take empowers them to safeguard their oral health and that of their close contacts.
Recommended: What Antibiotics Treat Gallbladder Infections?
6. Mindful Behavior in Close Contacts
Encouraging mindful behavior in close contacts can significantly reduce the risk of transmitting gum disease. While affectionate gestures like kissing can’t be avoided entirely, maintaining good oral hygiene practices and being cautious about sharing items that come into contact with the mouth can help mitigate bacterial exchange.
7. Seeking Professional Help
Lastly, the importance of seeking professional dental help at the onset of any oral health concerns cannot be overstated. Early intervention and professional guidance can prevent the progression of gum disease and reduce the risk of spreading oral bacteria to others.

Treatment and Management Of Gum Diseases
Addressing gum disease involves a multifaceted approach that aims to halt its progression, manage its effects, and restore oral health. Various treatment modalities and management strategies exist to combat gum disease effectively.
1. Professional Dental Care
Seeking professional dental care is crucial for the effective treatment of gum disease. Dentists or periodontists assess the severity of the condition and tailor treatment plans accordingly.
Professional cleanings, scaling, and root planing are common procedures that help remove plaque, tartar, and bacteria from the teeth and beneath the gum line.
Recommended: Vicks Vaporub for Gum Disease: Does It Work?
2. Antibacterial Therapy
In cases where gum disease has progressed significantly, antibiotics may be prescribed to combat the infection. These antibiotics can be administered in various forms, such as oral tablets, mouth rinses, or gels applied directly to the affected areas, to target and eliminate the bacterial infection.
3. Surgical Interventions
Advanced stages of gum disease may necessitate surgical interventions. Procedures like flap surgery, bone grafts, tissue regeneration, or gum grafting can help repair damaged tissues, reduce pocket depths, and restore the supportive structures around the teeth.
4. Ongoing Maintenance
After initial treatment, ongoing maintenance is crucial to prevent recurrence or progression of gum disease. Regular dental visits for follow-up evaluations and cleanings are essential. Patients are often advised on personalized oral hygiene routines and encouraged to adhere to them diligently.
5. Lifestyle Modifications
Making lifestyle modifications plays a significant role in managing gum disease. Quitting smoking or tobacco use can greatly improve the outcomes of treatment. Additionally, adopting a balanced diet and managing systemic health conditions like diabetes can contribute to better oral health outcomes.
6. Patient Education and Support
Educating patients about the importance of consistent oral care, the significance of follow-up appointments, and the role of lifestyle factors in gum disease management is crucial. Empowering individuals with knowledge equips them to actively participate in their oral health journey.
Recommended: Can You Get STD From Toilet Water Splashing?
7. Continuous Monitoring
Gum disease is a chronic condition that requires continuous monitoring. Regular evaluations by dental professionals help track progress, identify any signs of recurrence, and make necessary adjustments to the treatment plan if needed.
FAQs
Is gum disease contagious?
Yes, gum disease can be contagious. The bacteria responsible for gum disease, like periodontitis, can be transmitted through saliva. This happens through activities like sharing utensils, kissing, or even sharing a toothbrush.
Can I catch gum disease from someone else?
It’s possible. While it’s not as direct as catching a cold, the bacteria that cause gum disease can transfer between people through saliva. Close contact or sharing items that come into contact with saliva can potentially spread these bacteria.
How likely am I to get gum disease from someone else?
The likelihood varies. Factors like the health of your gums, oral hygiene practices, and overall health can affect susceptibility. However, regular oral hygiene, such as brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups, can significantly lower the risk of acquiring gum disease from others.
Can I spread gum disease to my family?
Yes, it’s possible. Family members who share close contact, utensils, or items that come into contact with saliva may be at risk of acquiring the bacteria that cause gum disease. Maintaining good oral hygiene and being aware of sharing habits can help reduce this risk.
Can I get gum disease from kissing someone with gum disease?
It’s a potential risk. Kissing can transfer bacteria from one person’s mouth to another’s, increasing the chance of contracting gum disease. However, maintaining good oral hygiene can mitigate this risk.
Can I prevent the spread of gum disease to others?
Yes, maintaining good oral hygiene is key. Regular brushing, flossing, using mouthwash, and visiting the dentist for check-ups can reduce the bacteria in your mouth, lowering the risk of transmitting gum disease to others.
What precautions should I take if someone close has gum disease?
Avoid sharing items that come into contact with saliva, such as utensils, toothbrushes, or cups. Encourage the person to seek dental treatment and practice good oral hygiene to reduce the risk of spreading gum disease.
Is it safe to share oral care products with someone who has gum disease?
It’s best to avoid sharing oral care products. Sharing toothbrushes, floss, or other oral hygiene items can increase the likelihood of transferring bacteria that cause gum disease.
Can gum disease spread through casual contact, like shaking hands?
No, gum disease doesn’t spread through casual contact like shaking hands. It requires direct contact or exchange of saliva-infected items for transmission to occur.
What should I do if I suspect I’ve been exposed to gum disease?
Focus on your oral hygiene. Consult a dentist for advice and consider scheduling a check-up to ensure your gums are healthy. Practicing good oral hygiene can mitigate the risk of developing gum disease after exposure.
Conclusion
Understanding the contagious nature of gum disease underscores the importance of proactive oral care and preventive measures. By prioritizing good oral hygiene, seeking professional dental care, and being mindful of close contact, people can significantly reduce the risk of spreading gum disease.
Empowerment through knowledge and consistent oral health practices serves as the key to safeguarding not just personal oral well-being but also that of those around us.
[…] See also Is Gum Disease Contagious? […]
[…] Recommended: Is Gum Disease Contagious? […]
[…] See also Is Gum Disease Contagious? […]
[…] Recommended: Is Gum Disease Contagious? […]
[…] Recommended: Is Gum Disease Contagious? […]